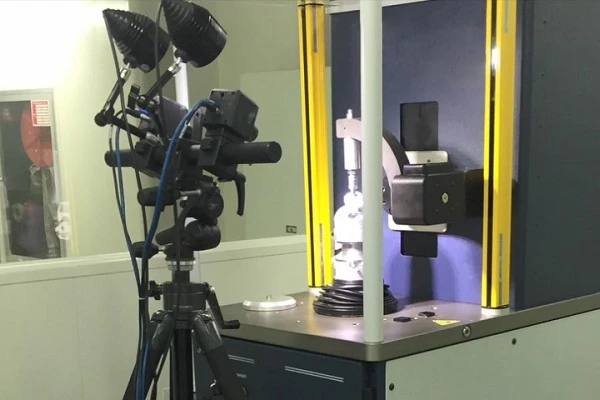
Biomedical engineering is an interdisciplinary scientific field aimed at improving human health and medical care. From an engineering perspective, biomaterials, mechanobiology, and biofabrication interact with target biological systems to achieve various medical therapeutic goals. Digital image correlation (DIC) technology, as a non-contact, precise, efficient, and non-destructive full-field strain measurement method, can be used to measure the mechanical properties and behavior of complex mechanobiology, biomaterials, bioprinting, and fabrication processes.
Biomaterials often have complex shapes. Measuring soft tissues or complex skeletal structures under load is challenging using contact sensors, especially due to the need for contact sensors to connect and contact the sample throughout the experiment. In some cases, contact sensors may even affect the material properties.
Digital image correlation (DIC) technology, an easy-to-use, non-contact measurement method, can address these application challenges. Furthermore, DIC allows for high-precision full-field profile, displacement, and strain measurements of objects. DIC provides thousands of measurement points, helping researchers understand the complex interactions between the physical properties of the test piece under load and obtaining high-quality experimental data to validate and optimize computer models.